Oseltamivir Phosphate (Oseltamivir phosphate) is often referred to as "Tamiflu" (Tamiflu). Produced and sold by the Roche Group, launched in Switzerland in 1999, and launched in China in 2001. It is the most commonly used and one of the most effective drugs against avian influenza, H1N1 influenza virus and influenza B virus. Reducing the incidence of influenza complications can also reduce the use of other medicines, and Tamiflu can increase the survival rate of influenza patients by about 37%.
But it also has large side effects, especially for children. And its price is more expensive to take twice a day, 75mg each time, the retail price of medicines is equivalent to 60 yuan per day, and a course of 5 days is equivalent to about 300 yuan. In addition, taking Tamiflu before the flu has no preventive effect on flu.
Oseltamivir Phosphate,Oseltamivir Phosphate Ingredients,Oseltamivir Phosphate Para Que Sirve,Oseltamivir Phosphate Over The Counter Jinan Prosperity International Trade Co. Ltd , https://www.cnsrtrade.com
1. Purpose and principle High-efficiency filter After the on-site installation, the leak detection is to confirm the high-efficiency filter and the installed static pressure box. No leakage or trace leakage is found within the scope of the specification. If the high-efficiency filter device is qualified for leak detection, it can ensure the safe and reliable operation of the clean room. When the indoor cleanliness is still not up to standard, the cause should be found from other aspects of the clean room.
Leak detection after high efficiency filter installation is different from the efficiency test of the filter manufacturer in the factory. The latter only tests the efficiency of the filter and other related performance, while the former involves leaks caused by a variety of factors associated with high efficiency filters and installation.
Leak detection after high-efficiency filter installation is usually carried out in an empty state or static state. It is recommended to carry out the test after the air volume balance of the clean room and the positive and negative pressure adjustment. The newly built clean room or the replacement of the high-efficiency filter of the terminal should be tested for leak detection.
Article 3.4.4 of the “Code for Construction and Acceptance of Cleanrooms†(hereinafter referred to as “Specificationsâ€), “Immediately installed after passing inspection and leak detectionâ€, it means that it is difficult to install high-efficiency filters after the on-site leak detection is qualified. Such leak detection conditions are available. It is impossible to do so, and according to the requirements of Appendix 6 of the specification, the scanning method of the high-efficiency filter is leak-detected after installation.
In the case of leak detection, the aerosol is introduced from the upwind side of the high-efficiency filter, and at the same time, the scanning and leak detection is performed on the downwind side of the high-efficiency filter to detect the filter medium of the high-efficiency filter, the sealant filter frame, the gasket, and the like. There is no leakage.
The high-efficiency filter leak detection in the pipeline and in the air conditioner is not discussed here. Only the leak detection method of the high-efficiency filter installed in the clean room terminal and related purification equipment is briefly discussed.
2. The upstream aerosol of the high efficiency filter introduces the polydisperse phase aerosol produced by the cold fog method into the upwind side air of the high efficiency filter. Make it to the desired aerosol concentration. The specification requires that particles larger than or equal to 0.5 μm be used. The aerosol materials are DOP (dioctyl phthalate), PAO (polyvinyl hydrocarbon), DOS (dioctyl succinate), etc. The principle of leak detection of these aerosols is the same.
The specification requires that the particle concentration on the windward side of the high efficiency filter (≥0.5 μm) must be greater than or equal to 3.5×104 particles/L. In fact, dust is generated in the air conditioner, and the concentration on the windward side of the filter is difficult to meet the requirements. A sufficient amount of aerosol must be introduced, and dusting for a long time will affect the service life of the high efficiency filter. Therefore, the leak detection of the high-efficiency filter is preferred in the static pressure tank of the high-efficiency filter air supply port. If the condition is not met, it is also conceivable to introduce the aerosol of the DOP on the air supply pipe.
3. Isometric sampling is sampled in a velocity airflow. The sampling speed should be equal to the airflow velocity. Otherwise, the sampling concentration will be greater or less than the true concentration, that is, the airflow velocity is greater than the sampling velocity, and the sampling concentration will be greater than the true concentration. Otherwise, the airflow velocity is less than the sampling rate. Speed, the sample concentration will be less than the true concentration.
Assume that the actual section wind speed under the high efficiency filter is 0.45 m/s, and the calculation of the circular sampling port diameter Ds:
V×1/4×πDs=Fa2
Fa--instrument sampling, 28.3L/min=472cm3/s
V--filter surface wind speed 0.45m/s
Calculated Ds=36.5mm
In fact, the sampling port diameter of the instrument is 35mm or square 30×30mm. Of course, the sampling port can also be rectangular. The sampling speed at this time is calculated to be 0.49~0.52m/s, which can be considered as constant velocity sampling.
Calculated according to the formula in the International Standards Organization (ISO) test and test method for clean rooms and related controlled environments (ISO14644-3): Sr ≤ Cc × Ps × K × Dp × Fs / Np = 50 × 0.005% × 10 × In the 3.5×472/Np formula: Sr-probe scanning rate cm/s;
Cc-measured filter upwind aerosol concentration cm-3 (50 particles / cm3);
Ps-tested filter zui easy to penetrate particle size zui large allows the overall penetration rate;
PL-tested filter zui large allow leakage;
K - a factor indicating how many times the PL may be larger than Ps;
Dp - the size of the probe parallel to the scanning direction (cm), this paper uses a circular sampling tube, diameter 35mm;
Standard sample flow rate for Fs-discrete particle counters,
Fs = 472 cm3 / s (28.3 L / min);
Np-expected amount, a particle count value exhibiting a leak characteristic;
Calculated by:
Np=Cc×Ps×K×Fs
Np=Cc×Ps×K×Fs=50×0.005%×10×472=11.8, substituting Sr for Sr=Cc×Ps×K×Dp×Fs/Np
= 50 × 0.005% × 10 × 3.5 × 472 / 11.8 = 3.5 (cm / s)
The actual acquisition time of each measuring point is Ts=Dp/Sr=1s 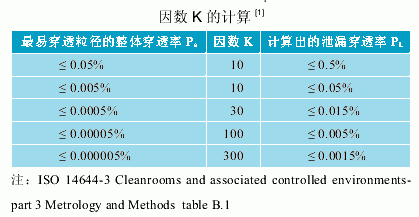
Therefore, the scanning rate of the sampling port is closely related to the upstream particle concentration penetration rate, the K value, the sampling port diameter, and the sampling flow rate. In particular, if you use a 28.3 L / min particle counter and a 2.83 L / min particle counter, their scan rate can be ten times different, that is, the time between each filter is also ten times different.
The specification requires a scan rate of 5 to 20 mm/s (in fact, this rate should be calculated and adjusted according to the specific situation. It is generally recommended to use a particle calculator of 28.3 L/min, and the scan rate is about 30 to 5 mm/s).
Article 5.4.1 of the Code states that “for high-efficiency filters, it shall be no more than 2 times the qualified transmission rate of the filter, and for ultra-high efficiency filters, it shall not be more than 3 times the qualified transmission rate of the factory.†According to the provisions In contrast to the fourth section, the high-efficiency filter has a transmittance of 3 times and the ultra-high efficiency filter is 2 times. From the data provided, the provisions should prevail.
If the upstream concentration is 3.5 × 104 particles / L, the high-efficiency filter efficiency of 0.5 μm is 99.99%, and the downstream concentration is 3.5 × 104 × 0.01% × 3 = 10.5. If the particle calculator detects ≤10, it should be qualified, otherwise it should be repaired. The total repaired area should not exceed 5% of the filter cross-section. The large length of each repaired patch must be below 40mm.
This article uses ISO14644-3 leak detection method and related calculations. As described above, Np is the number of particles of the table leakage characteristic, and when Np = 11.8, the observation count Ca = 7 is acceptable. In the leak detection, when the dust particle reading C ≤ Ca, it is considered that there is no leakage in the scanning area, and the scanning can be continued, otherwise, static measurement is to be performed. During static measurement, the retention time of the sampling head at the measuring point is set to 10 seconds. At this time, the measured large number of zui particles is Npa: Npa=Cc×PL×FS×K=50×0.005%×10×472× 10=118
This is the reading value when the sampling flow rate is 472cm3/s and the sampling time is 10s. If it is greater than this number, it can be judged as leakage.
If the total air volume of the system is not large, DOP dust can be sent directly to the total duct. If the total amount of DOP dust is not enough to meet the expected concentration requirements, the DOP can be directly sent to the static pressure tank of the high efficiency air supply port. It should be noted that the upstream aerosol concentration needs to be detected. If stabilized, leak detection can be performed on each filter. If the upstream aerosol concentration is too high, the particle counter cannot be detected and can be measured by dilution.
In the detection, if there are too many indoor interference factors, in order to eliminate the interference, the isolation cover can be added at the outlet of the tuyere, and the detection is performed in the cover, so that the detected data is more accurate.
In particular, the leak detection between the filter and the mounting frame can be leaked along the mounting frame, or the leak can be detected on the section of the air supply box. However, to avoid interference from the airflow, avoid the cabinet. The ash on the interference, especially the sampling port can not touch the frame of the high efficiency air inlet box or filter.
When the DOP leak detection is performed on the upper side of the high efficiency filter, the DOP introduction device and the concentration detection tube must be provided on the windward side of the high efficiency filter. These two tubes can also be used to detect the resistance of the filter.
(1) Leak detection must be performed after the high-efficiency filter is installed;
(2) Calculate the amount of dust generated by the DOP and the system air volume, and determine the DOP import location;
(3) To measure the particle concentration upstream of the high efficiency filter;
(4) According to the specification, the leak detection is performed at a particle size of 0.5 μm, and it is necessary to determine the correct K value. If a particle size other than 0.5 μm is used for leak detection, it is recommended to determine the K value according to the ISO 14644-3 standard;
(5) It is recommended to use a particle counter of 28.3 L/min for leak detection. If a particle counter of 2.83 L/min is used, the scanning speed must be controlled.
Introduction of on-site leak detection method after high-efficiency filter installation
With the wide use of clean rooms, there are more and more requirements for on-site leak detection after installation of high-efficiency filters in clean rooms. In fact, according to the provisions of Cleanroom Construction and Acceptance Specifications (JGJ71-90), high-efficiency filtration is carried out. There are many problems to be discussed in the installation site of the device.