1 Introduction Solid-liquid suspension is carried out under mechanical agitation. The basic purpose of solid-liquid agitation is to generate and maintain a suspension and to enhance the mass transfer between the liquid and solid phases. Solid-liquid agitation is usually divided into the following parts: (1) suspension of solid particles; (2) resuspension of settled particles; (3) infiltration of suspended particles into liquid; (4) use between particles and between particles and paddles The force causes the particle agglomerates to disperse or control the particle size; (5) the mass transfer between the liquid and solid.
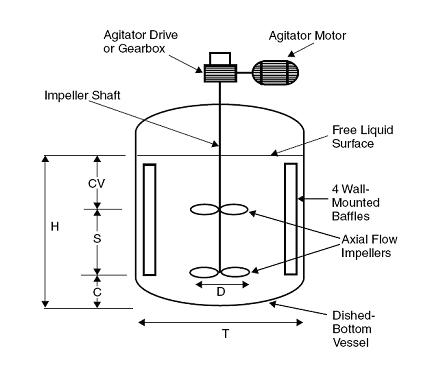
A typical solid-liquid mixing device is shown below.
2 Main factors affecting solid-liquid systems The properties of solid particles and liquids affect fluid flow and particle suspension. The geometry of the tank and the parameters of the agitator also have the same important influence. To sum up, these factors include:
2.1 The physical properties of the liquid include density, solid-liquid density difference and viscosity.
2.2 Physical properties of solids include density, particle size, geometry and sphericity, wetting properties, ability to capture external gases, agglomeration properties, and hardness and friction properties.
2.3 Process operating conditions include the depth of the liquid in the tank, the particle concentration, the volume fraction of the particles, and the presence or absence of bubbles.
2.4 Geometric parameters Including the groove diameter, the geometry of the bottom of the groove (flat bottom, round bottom, elliptical bottom, cone bottom), the shape and geometry of the agitator, the installation position of the agitator and the number of blades.
2.5 Stirring conditions include the stirrer's rotation speed, stirring power, paddle end line speed, suspension level, liquid flow pattern and distribution of turbulence intensity in the tank.